Chemistry for greenhouse gases Novel metal catalysts may be able to turn greenhouse gases into liquid fuels without producing more carbon waste Liviu Mirica (left), assistant professor of chemistry in Arts &The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, nitrous oxides, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) On Earth, human activities are changing the natural greenhouseMethane is the next of the greenhouse gases which has the biggest effect on global warming (15%) This is generated by activities such as livestock production, agriculture, sewage treatment, natural gas and oil distribution , coal mining, fuel use and is also given off from waste tips
Green House Effect
Gases responsible for greenhouse effect
Gases responsible for greenhouse effect-From 1990 to 19, the total warming effect from greenhouse gases added by humans to the Earth's atmosphere increased by 45 percent The warming effect associated with carbon dioxide alone increased by 36 percentGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear French mathematician Joseph




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
Carbon dioxide (CO2) Carbon dioxide is the primary greenhouse gas, responsible for about threequarters of emissions It can linger inIn general, fluorinated gases are the most potent and longest lasting type of greenhouse gases emitted by human activities There are four main categories of fluorinated gases—hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6 ), and nitrogen trifluoride (NF 3 )Most of the greenhouse gases are responsible to cause the greenhouse effect by radiating energy in all directions The earth's surface absorbs the most part of this radiation that results into its warming The strength of this effect depends upon the atmosphere's temperature and the amount of greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere
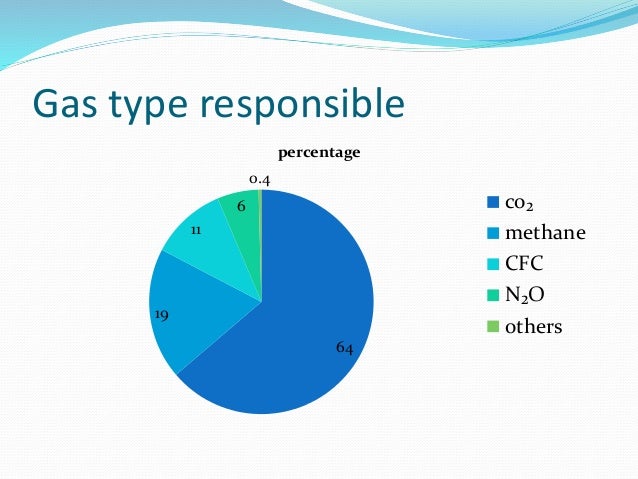
Explanation Greenhouse effect is the naturally occurring phenomenon that is responsible for heating of Earth's surface and atmosphere Carbon dioxide and methane are the biggest contributors of greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide and methane account for 564% and 163% greenhouse effect, respectively Ozone is responsible for 10%, nitrous oxide 54% and halocarbonsGreenhouse gases are gases in the Earth's atmosphere that produce the greenhouse effect Changes in the concentration of certain greenhouse gases, from human activity (such as burning fossil fuels), increase the risk of global climate change Greenhouse gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane, nitrous oxide, halogenatedIn terms of the net increase in the greenhouse effect due to humanproduced greenhouse gases, CO 2 is responsible for the lion's share CO 2 from fossil fuel burning alone is more than half the net force If you add CO 2 from fossil fuel burning, deforestation, and other minor sources, this comes to a little more than threefourths of the net
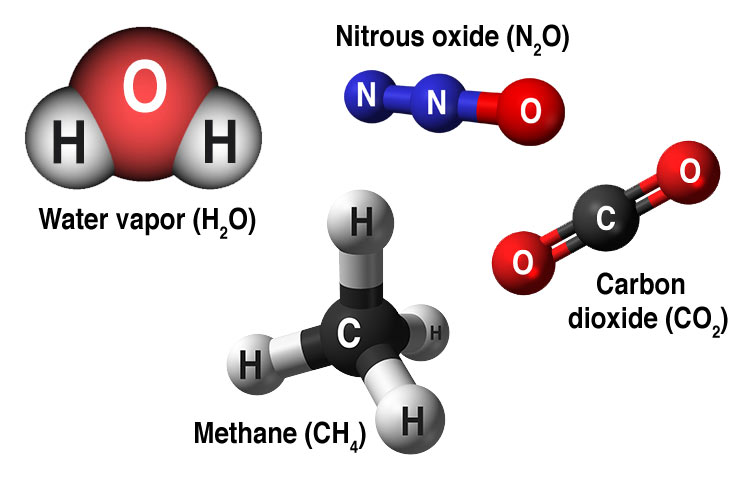
Water vapor feedback can also amplify the warming effect of other greenhouse gases, such that the warming brought about by increased carbon dioxide allows more water vapor to enter the atmosphere The difference in an atmosphere with a strong water vapor feedback and one with a weak feedback is enormous, Dessler saidModels showed that approximately 93% of crop losses over the rest of the century could be caused by non–carbon dioxide emissions, the mostGreenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and ozone (O 3) Other greenhouse gases have essentially no natural sources, but are side products of industrial processes or manufactured for human purposes such as cleaning agents



Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet



Controlling Industrial Greenhouse Gas Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
These gases are known as greenhouse gases Below are the most important greenhouse gases that influence Earth's climate system Water vapor (H2O) is the strongest greenhouse gas, and the concentration of this gas is largely controlled by the temperature of the atmosphere As air becomes warmer, it can hold more moisture or water vaporGreenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn't let that warmth escape That's exactly how greenhouse gases act They letGreenhouse Gases Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which makes the Earth warmer People are adding several types of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, and each gas's effect on climate change depends on three main factors



Global Warming And Mankind




Which Of The Following Is Not Responsible For Greenhouse Effect Att Ta Rata Hai Agerar 1878
Which Greenhouse Gas Does the Most Damage to Crops?Select Text Level 4 th Grade 6 th Grade 8 th Grade 12 th Grade The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3 ), and fluorinated gasesEstimated Reading Time 6 mins
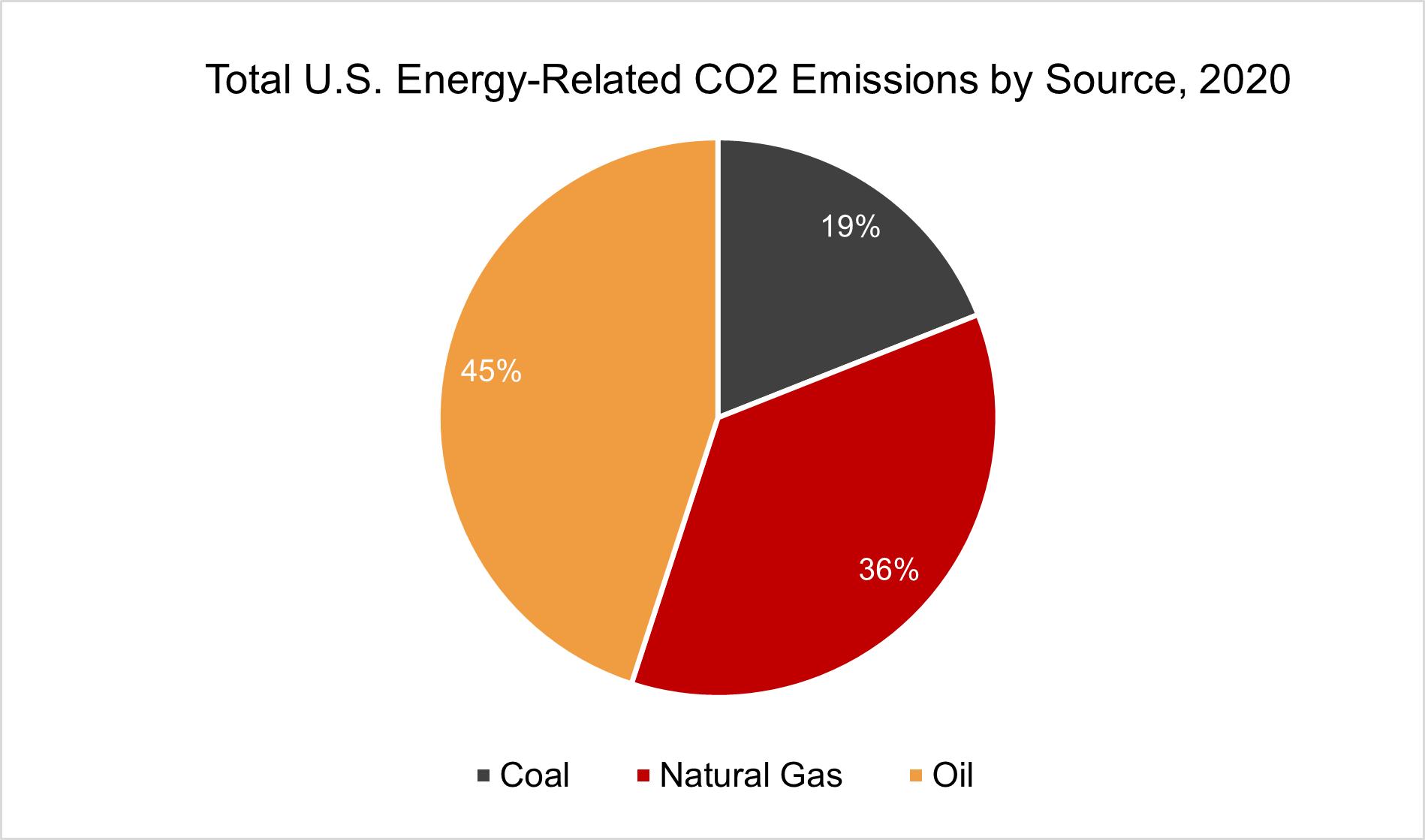



Fossil Fuels Eesi



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
Sciences, and Julia Khusnutdinova, a postdoctoral researcher in his lab, work together on a metal complexCarbon dioxide Of the greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the most prominent Sources of atmospheric CO 2 include volcanoes, the combustion and decay of organic matter, respiration by aerobic (oxygenusing) organisms, and the burning of fossil fuels, clearing of land, and production of cement by humansThe greenhouse effect keeps the temperatures on our planet mild and suitable for living things Greenhouse gases (GHG) include carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases These molecules in our atmosphere are called greenhouse gases because they absorb heat
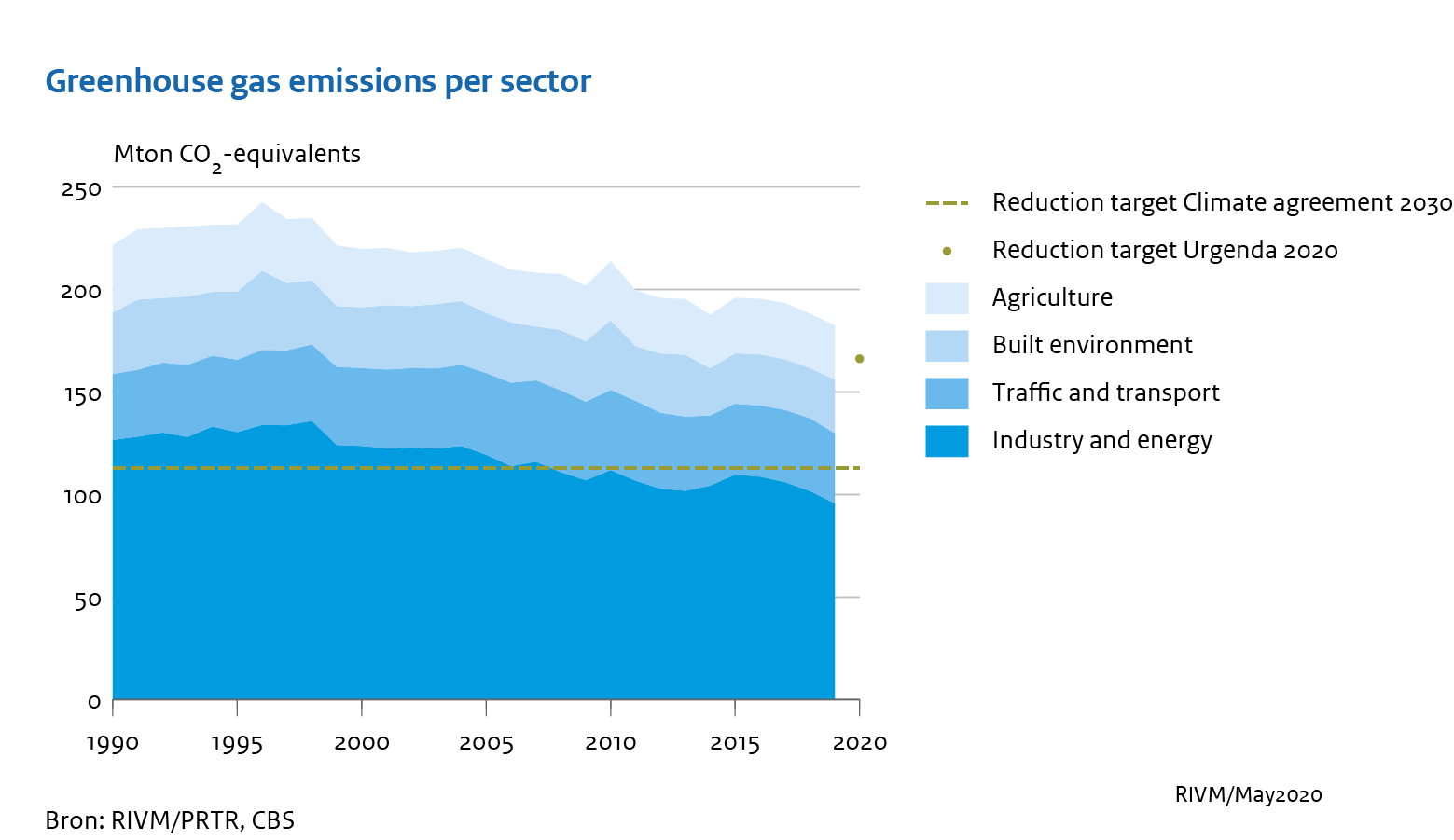



Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases Slightly Lower Again In 19 Rivm
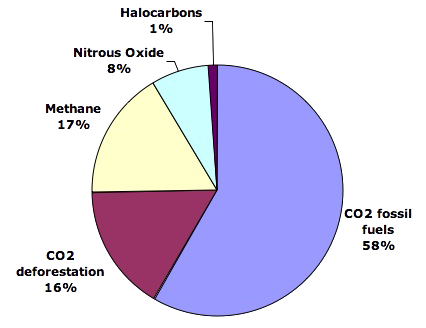



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici
The most wellknown greenhouse gas is Carbon Dioxide, also known as CO2 Other greenhouse gases are methane, carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrous oxide and water vapourLet's consider the principal GHGs one at a time, starting with water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere according to NOAA's National Climatic Data Center (NCDC) Water Vapor Carbon Dioxide (CO 2) Methane (CH 4) Nitrous oxide (N 2 O) Fluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) References and ResourcesChlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Synthetic compounds entirely of industrial origin used in a number of applications, but now largely regulated in production and release to the atmosphere by international agreement for their ability to contribute to destruction of




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia Republished Wiki 2
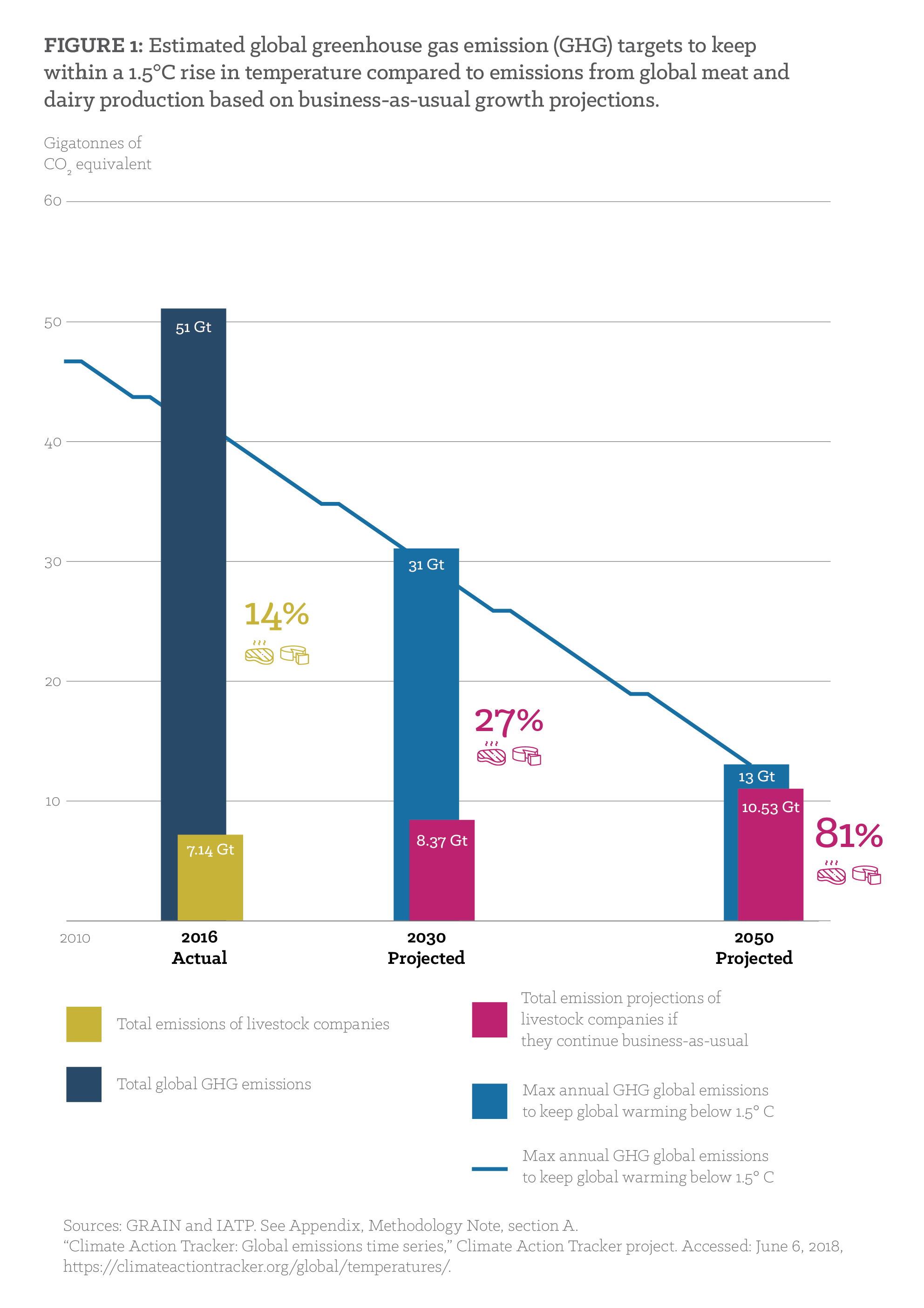



Grain Emissions Impossible How Big Meat And Dairy Are Heating Up The Planet
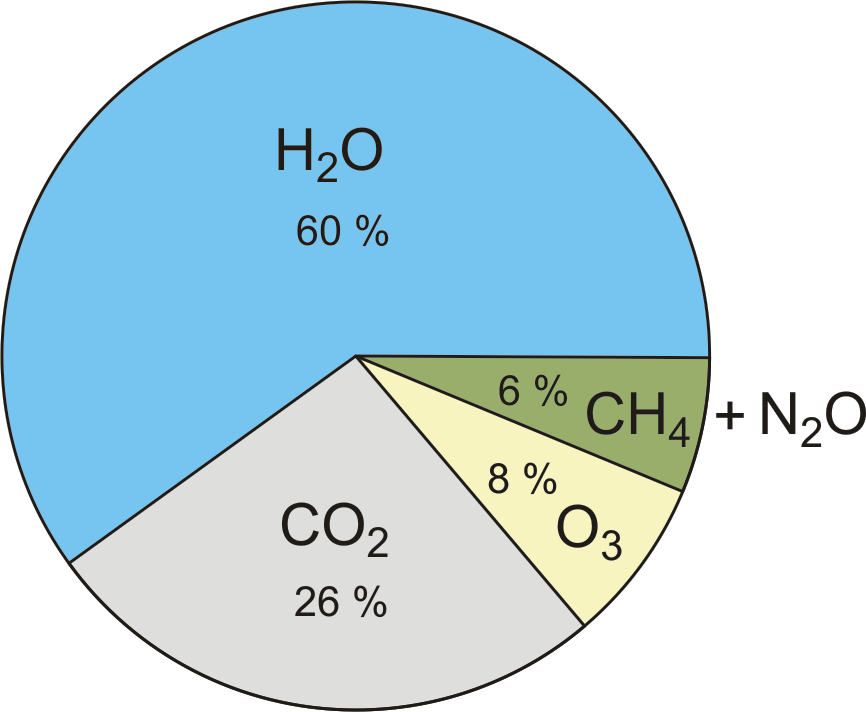
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3), and fluorinated gasesThe enhanced greenhouse effect What has scientists concerned now is that over the past 250 years, humans have been artificially raising the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere at an everincreasing rate, mostly by burning fossil fuels, but also from cutting down carbonabsorbing forestsCurrently, carbon dioxide accounts for more than 60 percent of the enhanced greenhouse effect caused by the increase of greenhouse gases, and the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is
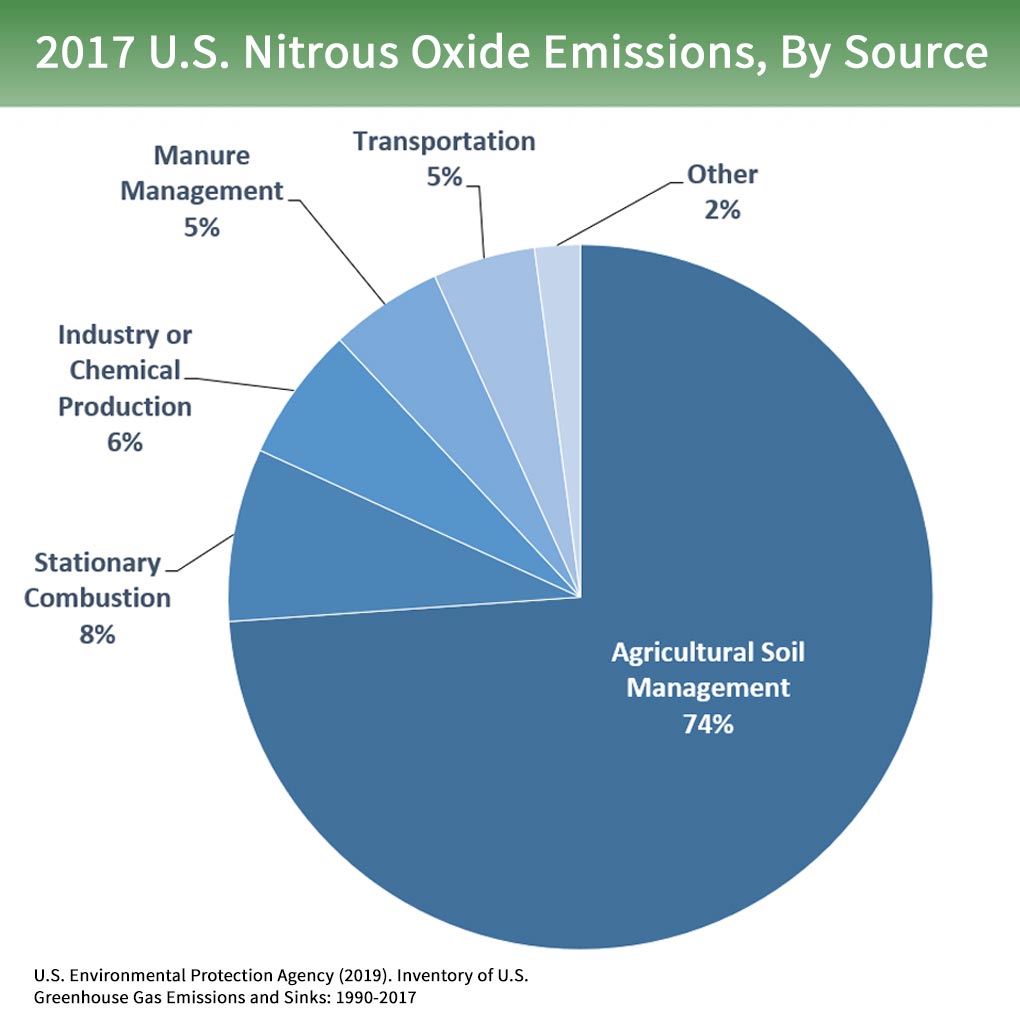



The Greenhouse Gas No One S Talking About Nitrous Oxide On Farms Explained Civil Eats




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
The result is Earth's temperatures higher than they would be in the absence of these gases The atmospheric gases and a greenhouse work in quite different ways, but the resulting effect, higher temperature in both cases, has led to the nomenclature "greenhouse gases" for the atmospheric gases responsible for the atmospheric warming effectThe greenhouse effect is not the same on all planets, and differs dramatically based on the thickness and composition of the atmosphereThree planets that show how dramatically the conditions of a planet can change with the different levels of the greenhouse effect are Venus, Earth, and Mars Earth, Mars, and Venus are different distances from the Sun Venus is theThe gases in the atmosphere that absorb radiation are known as greenhouse gases (abbreviated as GHG) because they are largely responsible for the greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect, in




Corporate Honesty And Climate Change Time To Own Up And Act Nrdc




Appetite For Change
Estimated Reading Time 7 minsThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsPart of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming itThe Greenhouse Effect The picture below shows the greenhouse effect Light from the sun passes through the atmosphere and is absorbed by the Earth's surface, warming it Greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, act like a blanket, trapping heat near the surface and raising the temperature It is a natural process that warms the planet




Global Warming And Climate Change The Science World Nuclear Association
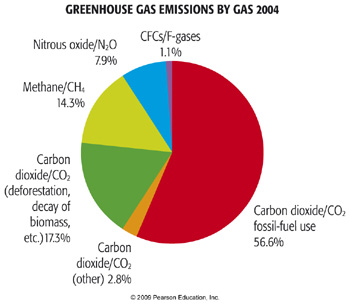



Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming
The most abundant greenhouse gases responsible for the greenhouse effect in the atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone These greenhouse gases keep the surface of the Earth approximately 60F warmer than we would expect without these gasesMost of these humancaused (anthropogenic) greenhouse gas emissions were carbon dioxide (CO2) from burning fossil fuels Concentrations of CO2 in the atmosphere are naturally regulated by many processes that are part of the global carbon cycleThe primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are CO 2, CH 4, water vapour, nitrous oxide, and ozone Greenhouse gases cause the greenhouse effect on earth by
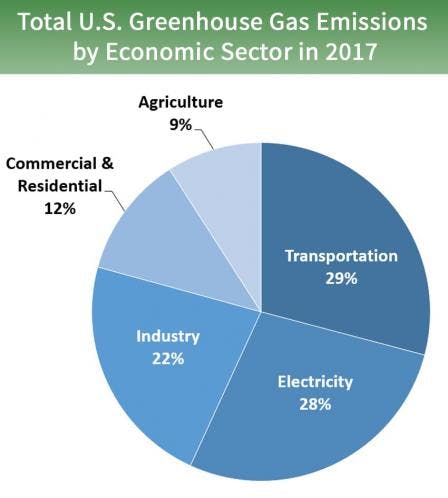



Climate Change Is The Symptom Consumer Culture Is The Disease The New Republic
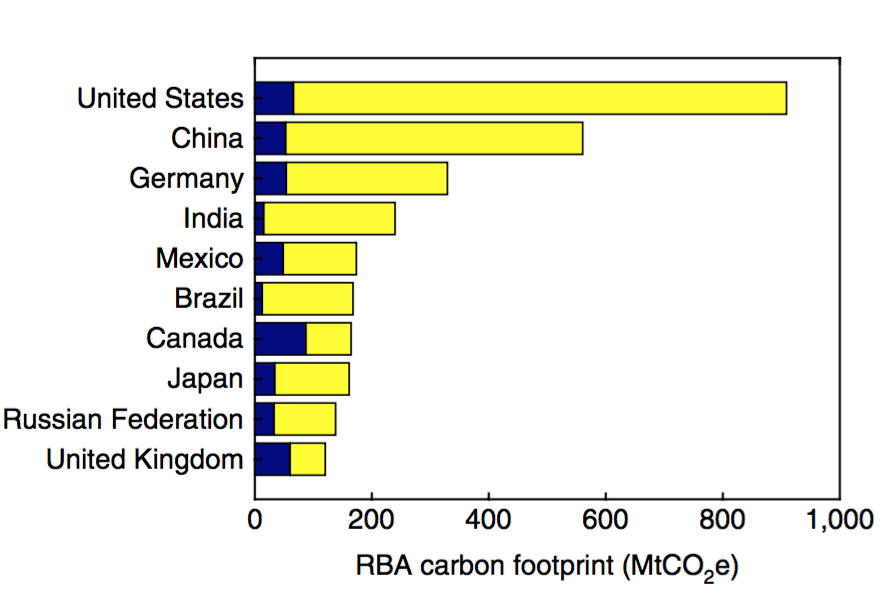



Tourism Responsible For 8 Of Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Study Finds Carbon Brief
Greenhouse gases are responsible for the Greenhouse Effect But before we investigate that, let's find out what greenhouse gases are Can you name any of them?8 rowsGreenhouse gas Chemical formula Global Warming Potential, 100year time horizon AtmosphericGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Scientists have determined that carbon dioxide's warming effect helps stabilize Earth's atmosphere Remove carbon dioxide, and the terrestrial greenhouse effect would collapse Without carbon dioxide, Earth's surface would be some 33 °C (59 °F) cooler



1




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
The greenhouse effect is a natural process responsible for keeping the earth at the temperature needed to sustain life Acting just like the glass walls of a greenhouse, gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide trap the sun's heat in the atmosphere and prevent itThe greenhouse effect accounts for global climate change, and carbon dioxide is one of the chief greenhouse gases responsible According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, carbon
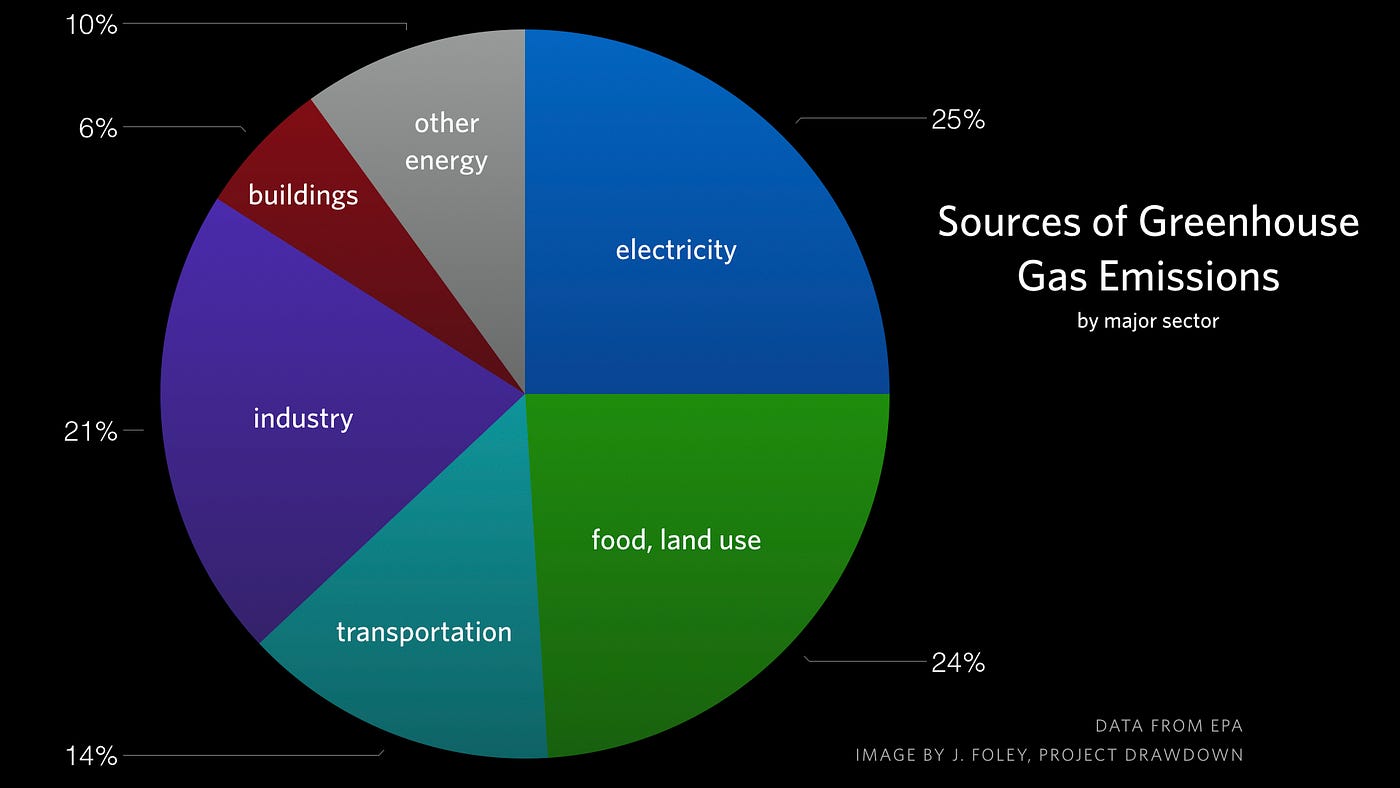



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org
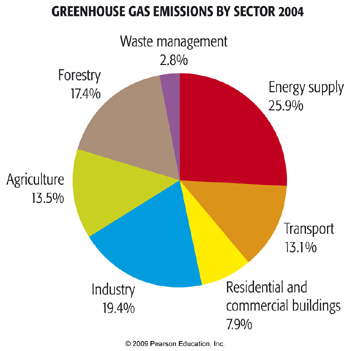



Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming




Appetite For Change




Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know




The Greenhouse Effect Mechanism



Greenhouse Gases




Global Warming Ppt Download




Which Nations Are Most Responsible For Climate Change Environment Theguardian Com
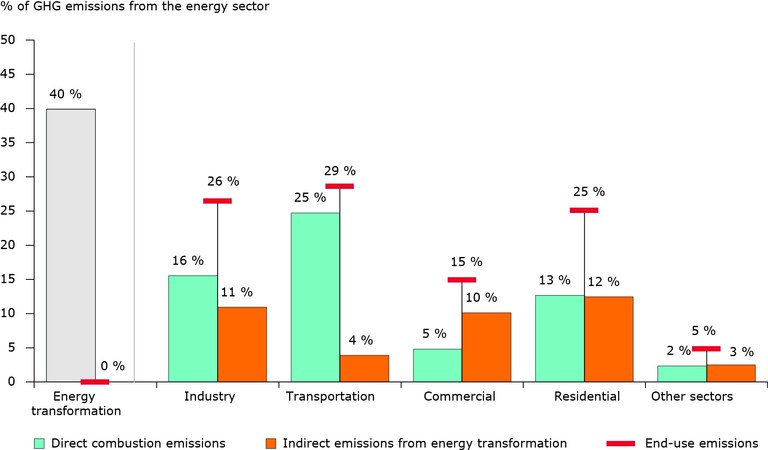



Households And Industry Responsible For Half Of Eu Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Fossil Fuels European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Domestic Hot Water Heat Pumps Compared To Most Commonly Used Systems Hong 16 Energy Science Amp Engineering Wiley Online Library



1




Causes Of The Greenhouse Effect Conserve Energy Future




Usgcrp Indicator Details Globalchange Gov




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa
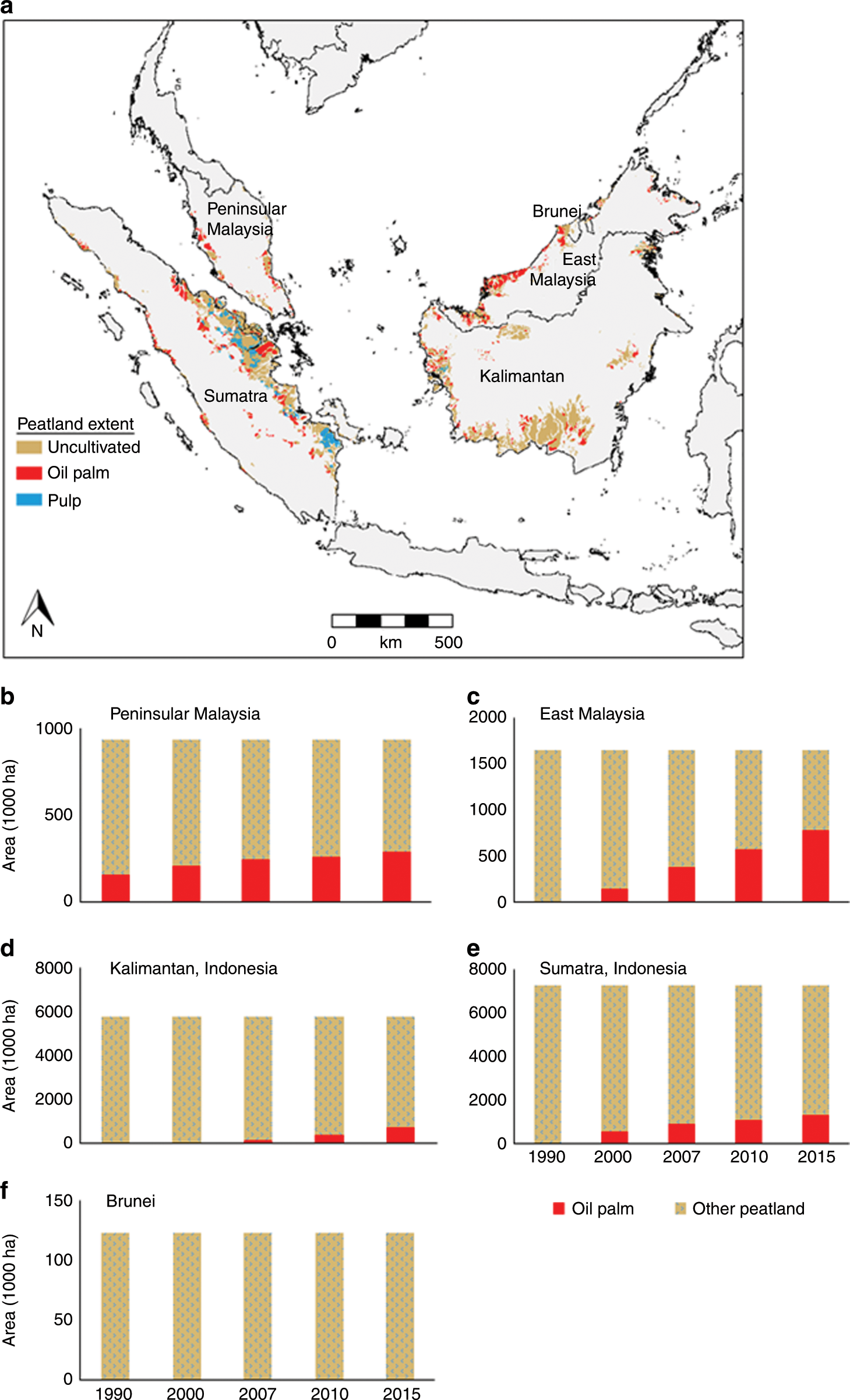



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Resulting From Conversion Of Peat Swamp Forest To Oil Palm Plantation Nature Communications




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research




Which Of The Following Pairs Of Gases Is Mainly Responsible For




What Is The Main Reason Of Global Warming Do Co2 Is Responsible Only Do Wildfire An Auto Event




What Are Greenhouse Gases Main Sources And Climate Impact
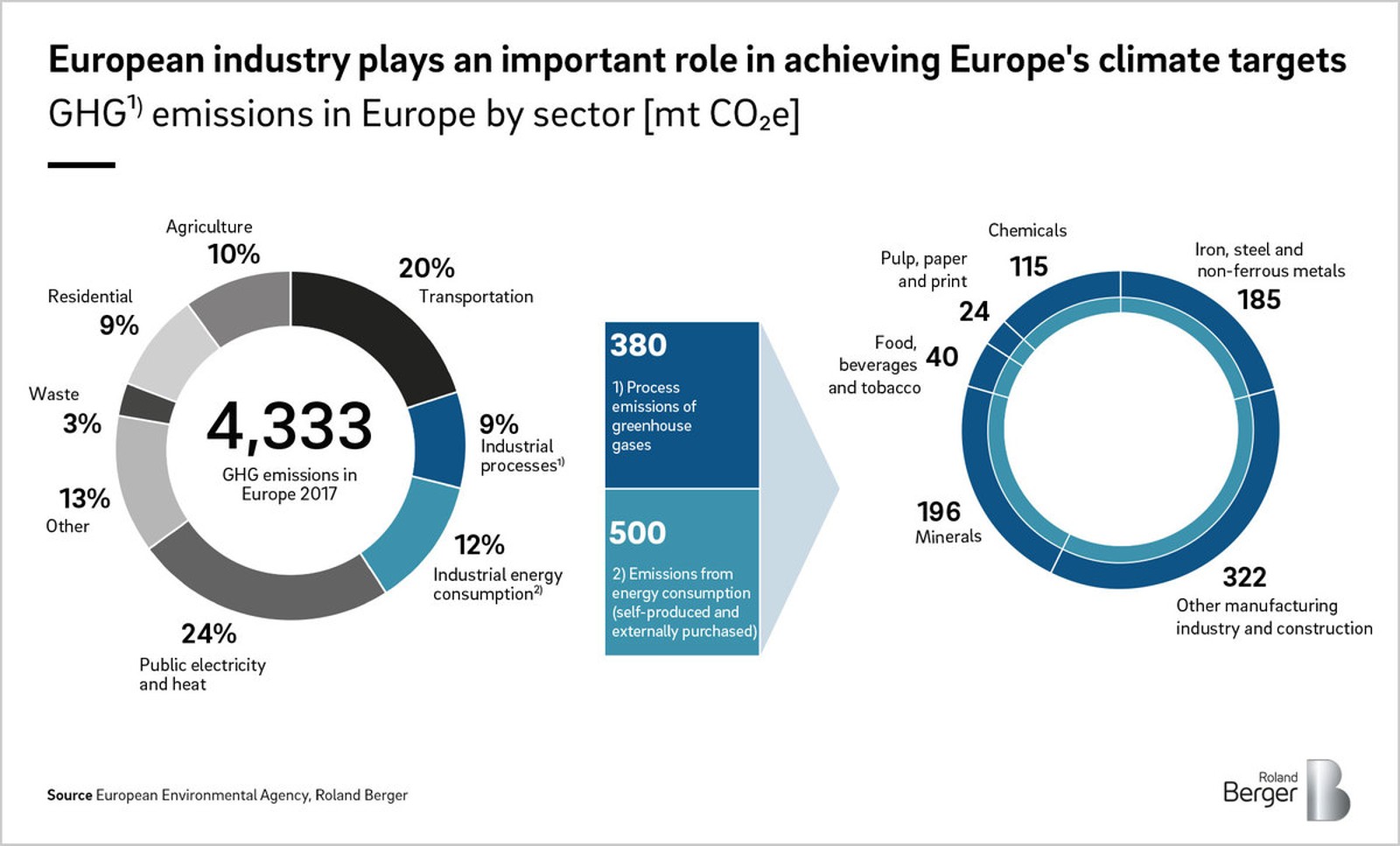



Reduzierung Von Co2 Klimaschutz Durch Emissionsarme Oder Neutrale Produktion In Deutschland Roland Berger



Library Wmo Int




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science




Solved 1 2ptsx 15 30pts Multiple Choice Choose The Best Chegg Com
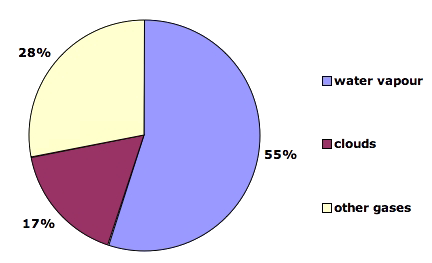



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




What Are Greenhouse Gases Domesticgoddessguidetocc




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




How To Stop Global Warming The 8 Best Solutions




Chemsolve Net What Are The Main Causes Of Global Warming In Points



Greenhouse Gases



1




Solved 23 Under The Greenhouse Effect Inct He Greenhouse Chegg Com




Cornell Biologists Aim To Grow Bugs Responsible For Greenhouse Gas Methane In Nsf Funded Microbial Observatory Cornell Chronicle




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
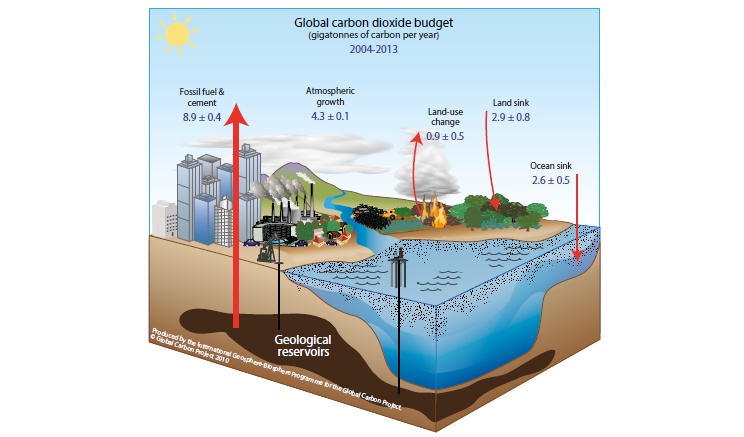



3 Are Human Activities Causing Climate Change Australian Academy Of Science
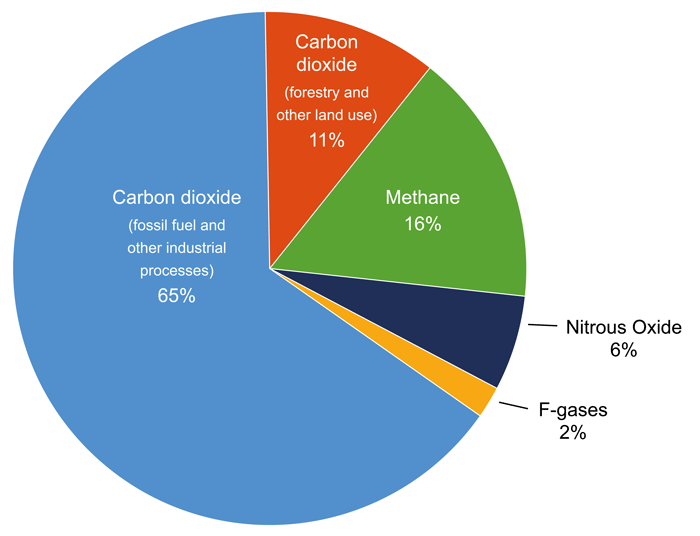



Causes Of Climate Change And Sea Level Rise Coastadapt




Contributions Of Natural Systems And Human Activity To Greenhouse Gas Emissions Sciencedirect
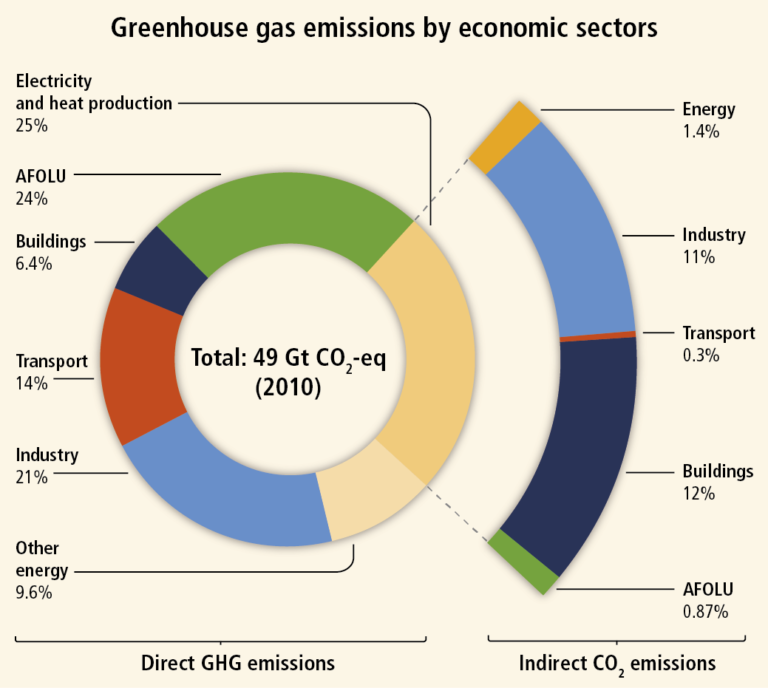



Impact Of Agriculture On Climate Change




V1003 Science And Society Sources And Impacts Of Greenhouse Gases
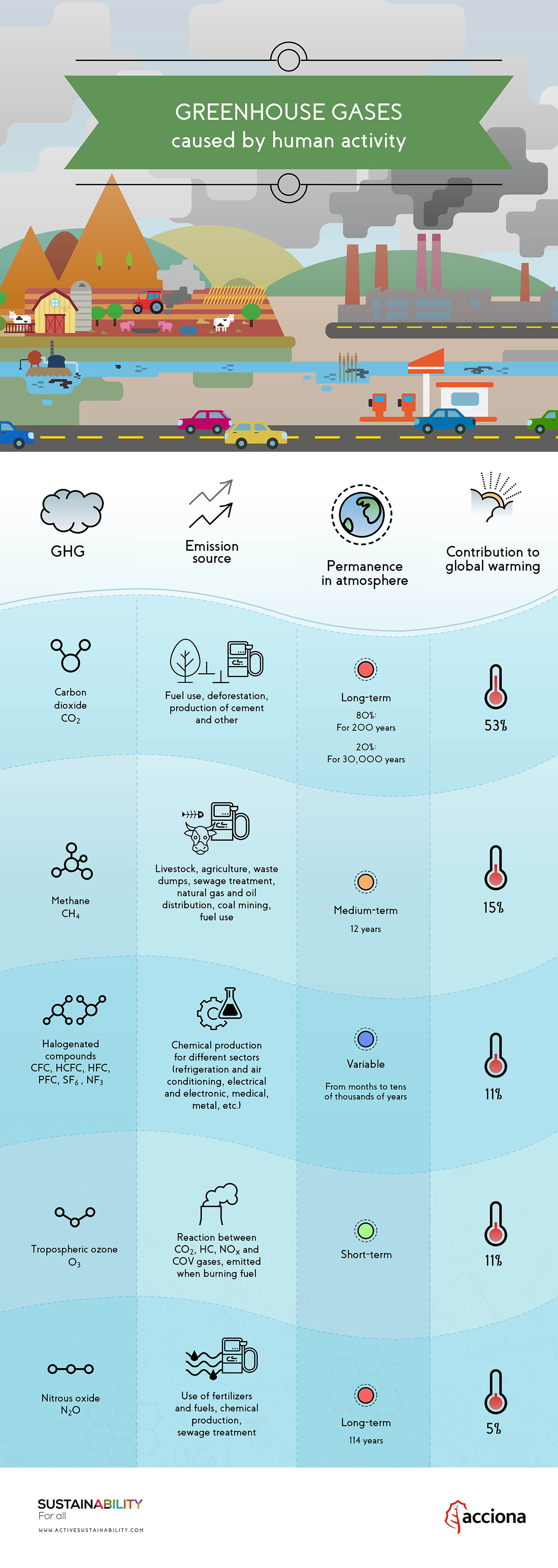



How Do Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data




Climate Literacy Quiz
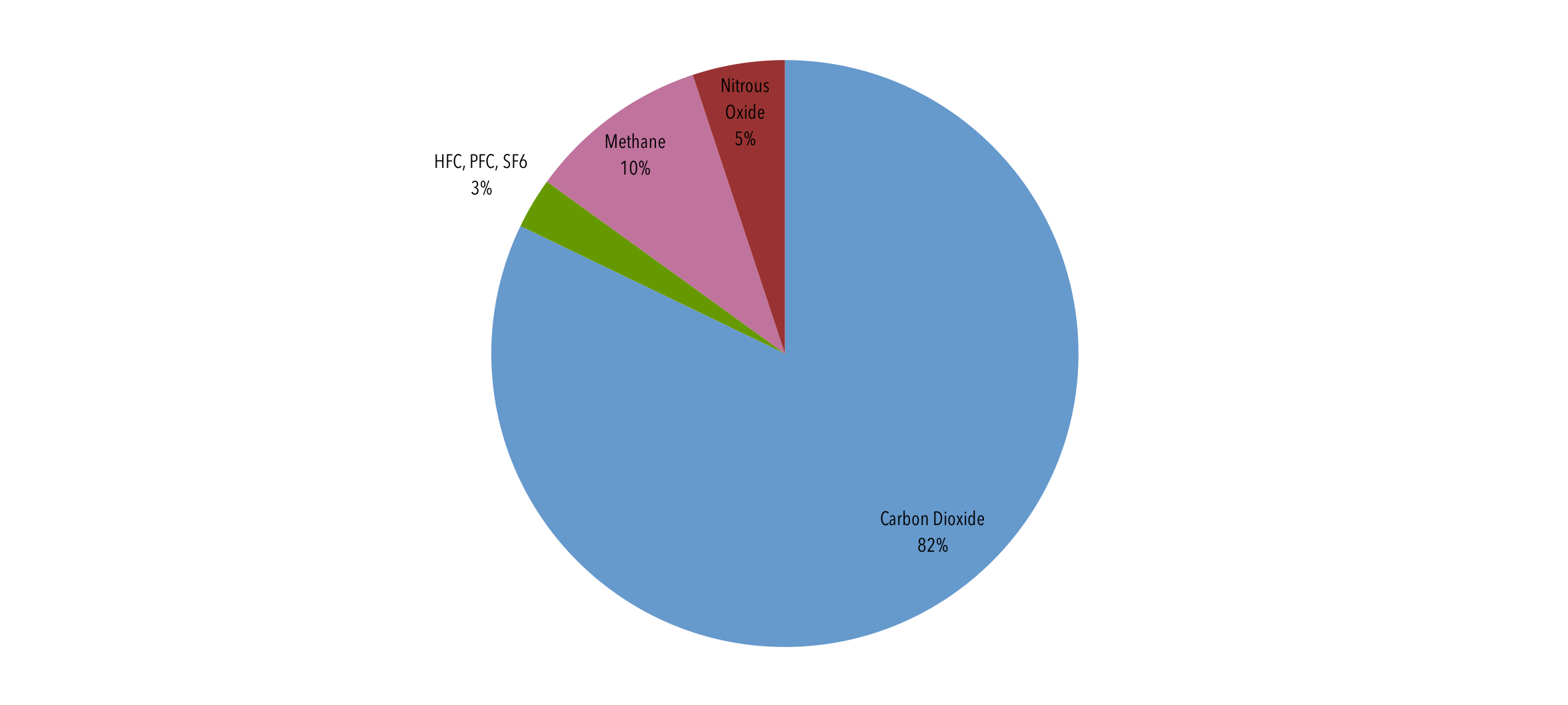



Short Lived Climate Pollutants Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
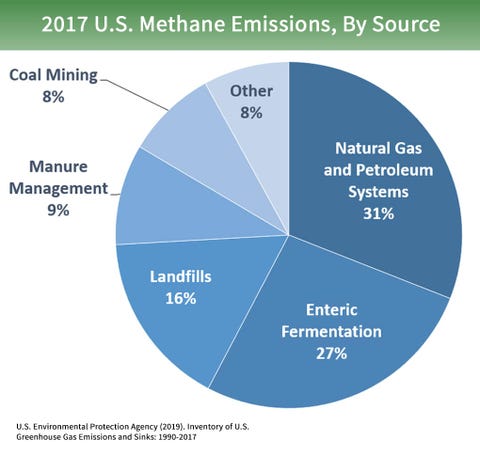



What Is Methane Methane Greenhouse Gas Facts




List The Gases Which Are Responsible For Greenhouse Effect




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Transport Could Burn Up The Eu S Entire Carbon Budget International Council On Clean Transportation



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
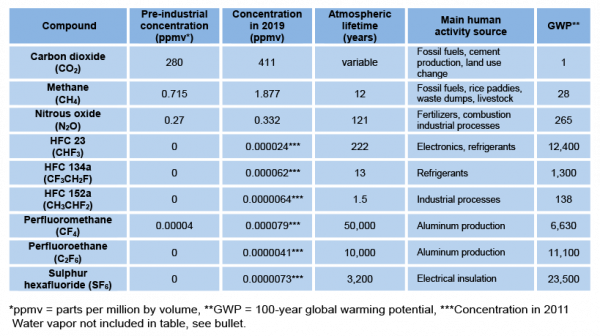



Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Carbon Intensive Industries The Industry Sectors That Emit The Most Carbon Eco Warrior Princess



Greenhouse Gas Emission Trends European Environment Agency
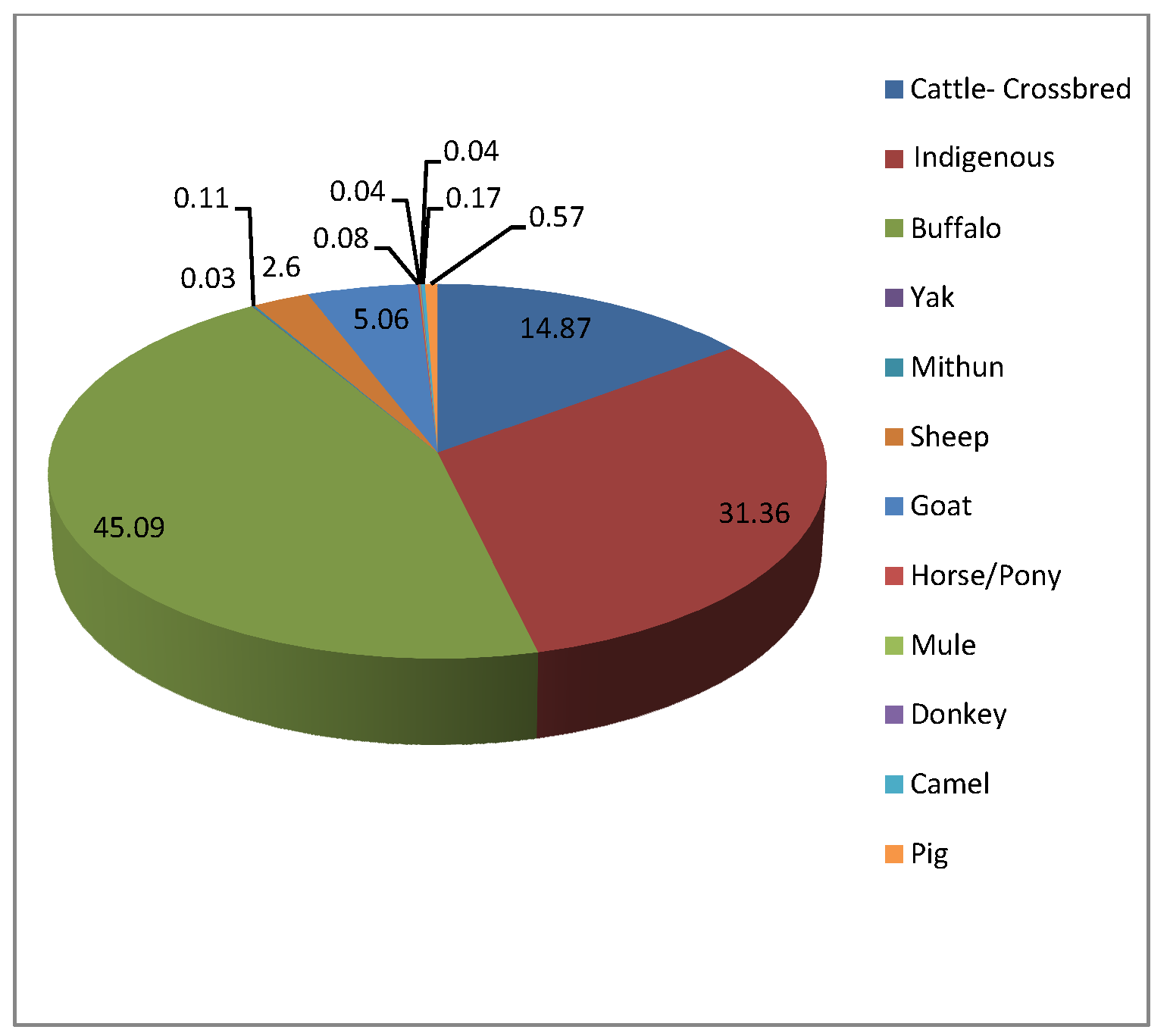



Livestock As Sources Of Greenhouse Gases And Its Significance To Climate Change Intechopen




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Germany S Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Energy Transition Targets Clean Energy Wire




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central




Green House Effect



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
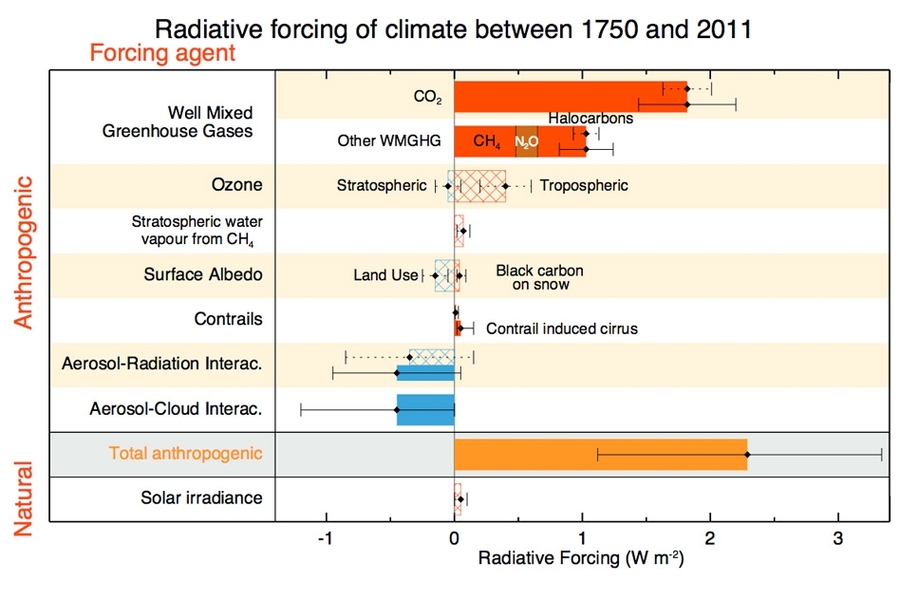



Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
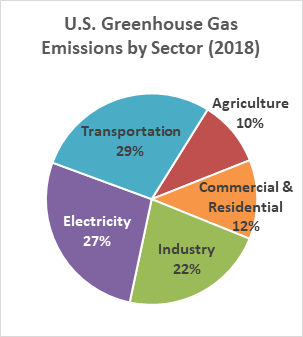



Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Global Warming Walkin On Fire Crash Course 03 The Major Culprit Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
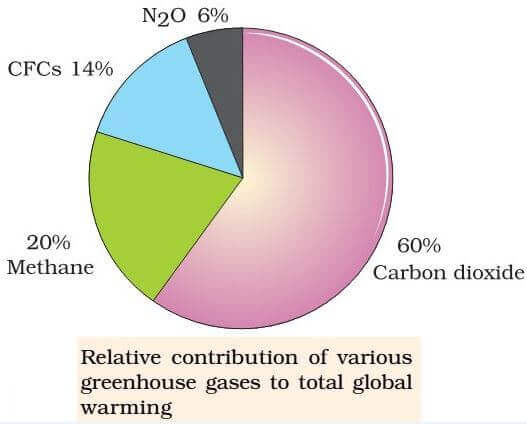



Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Carbon Sequestration Pmf Ias
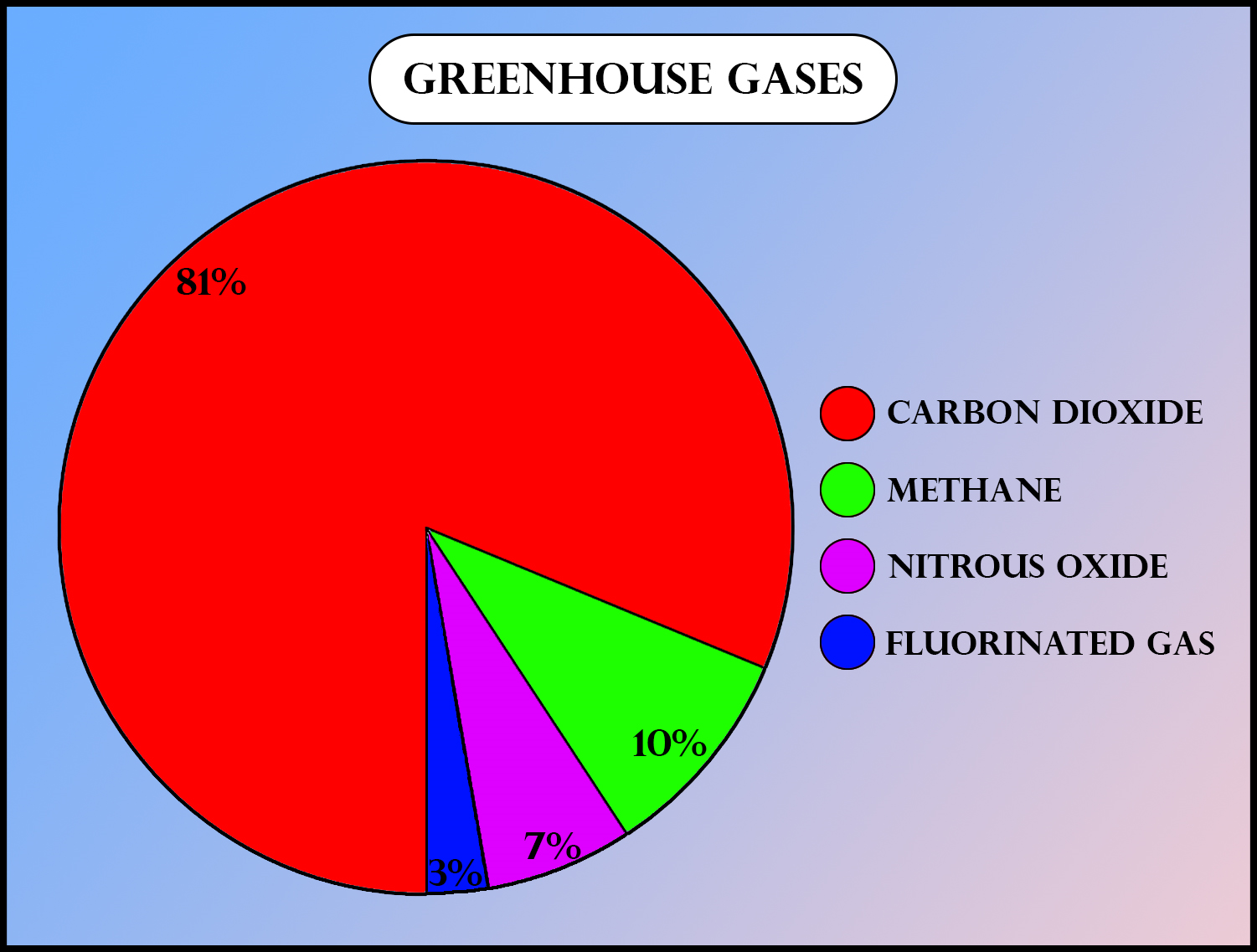



Which Of The Following Gas Is Responsible For Globalwarming Class 12 Biology Cbse
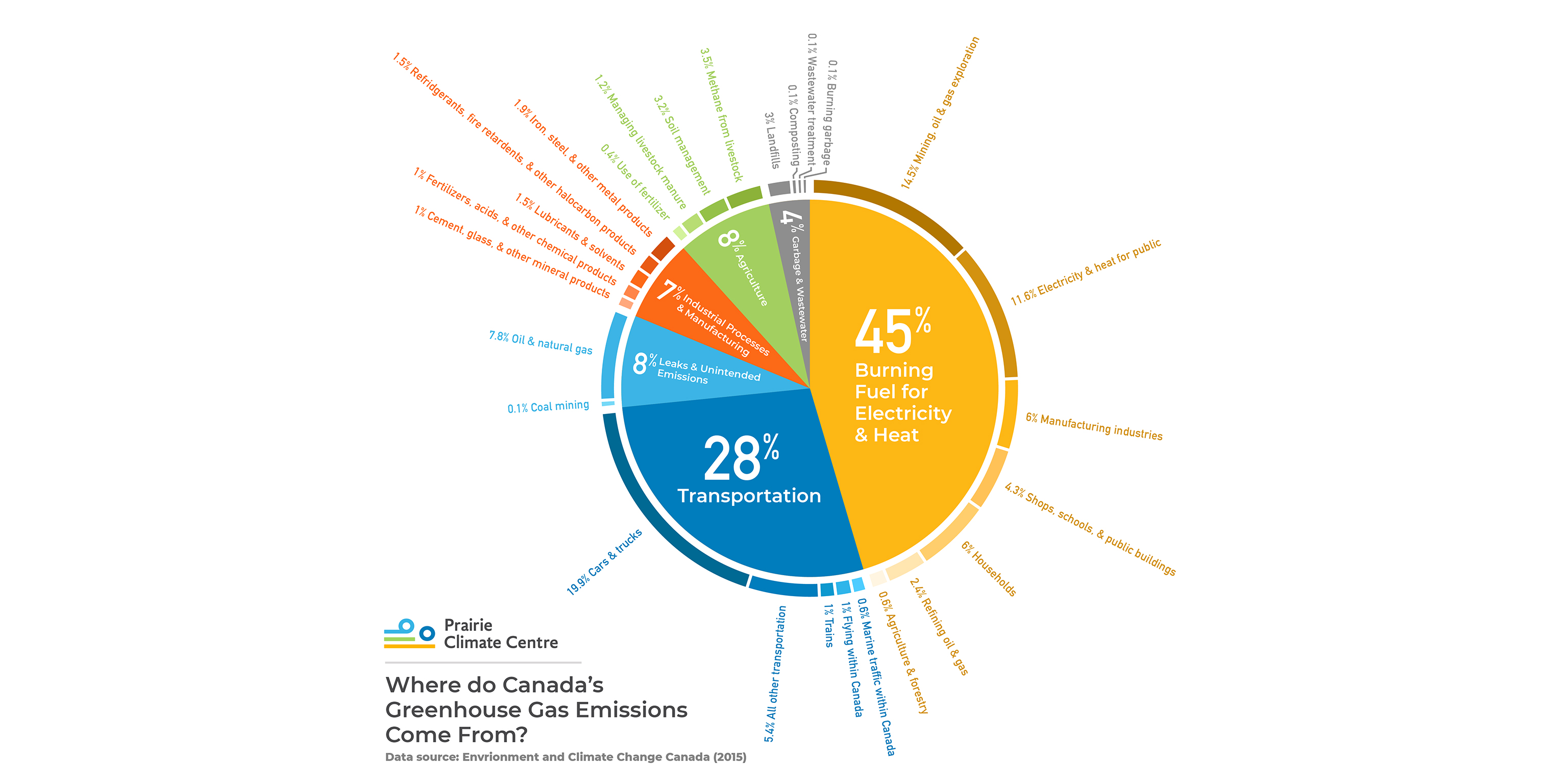



Where Do Canada S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From
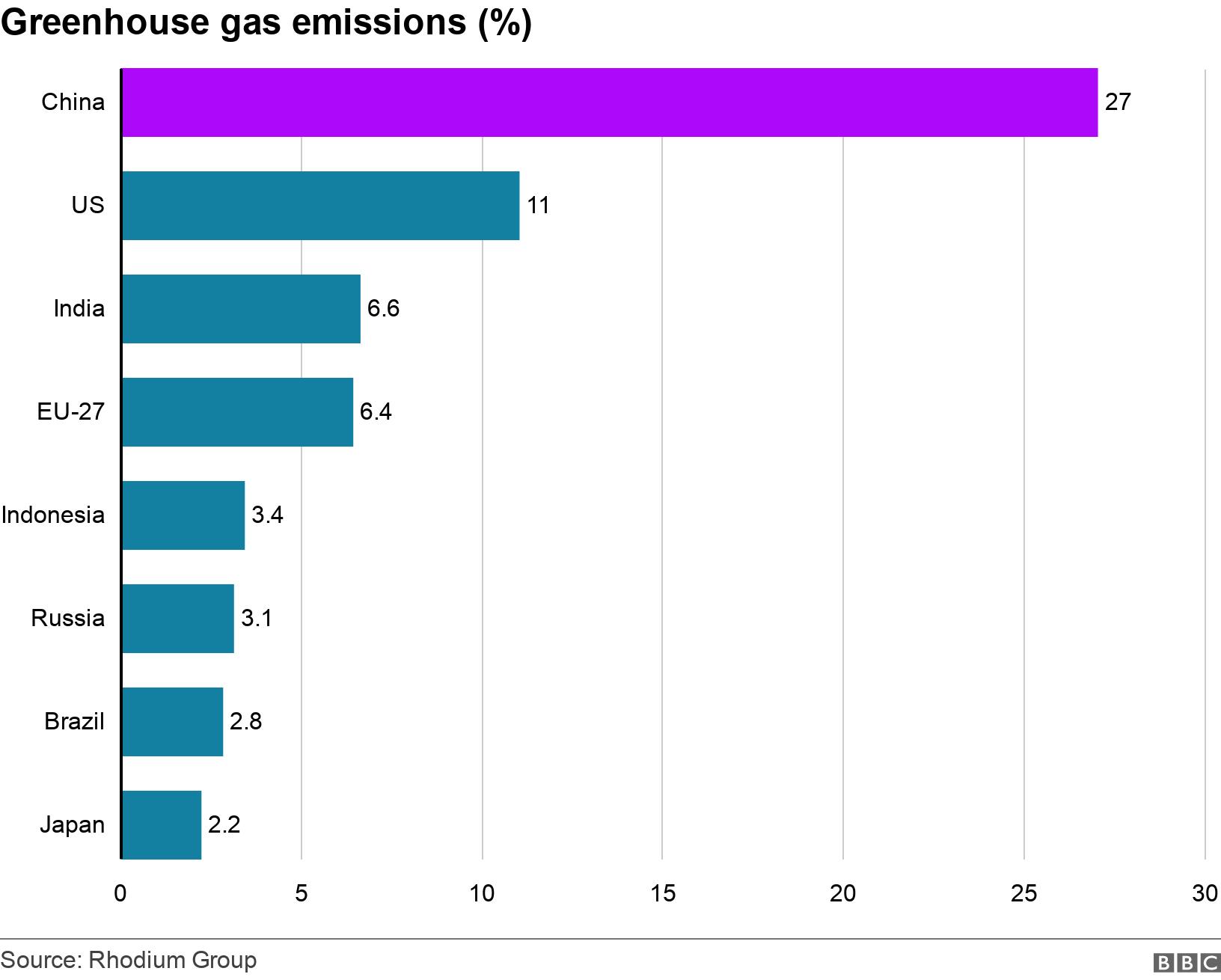



Report China Emissions Exceed All Developed Nations Combined c News




Food Production Is Responsible For One Quarter Of The World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



Developed Countries Are Responsible For 79 Percent Of Historical Carbon Emissions Center For Global Development




What Are Greenhouse Gases And Why We Need To Worry About Them A Simple Explainer
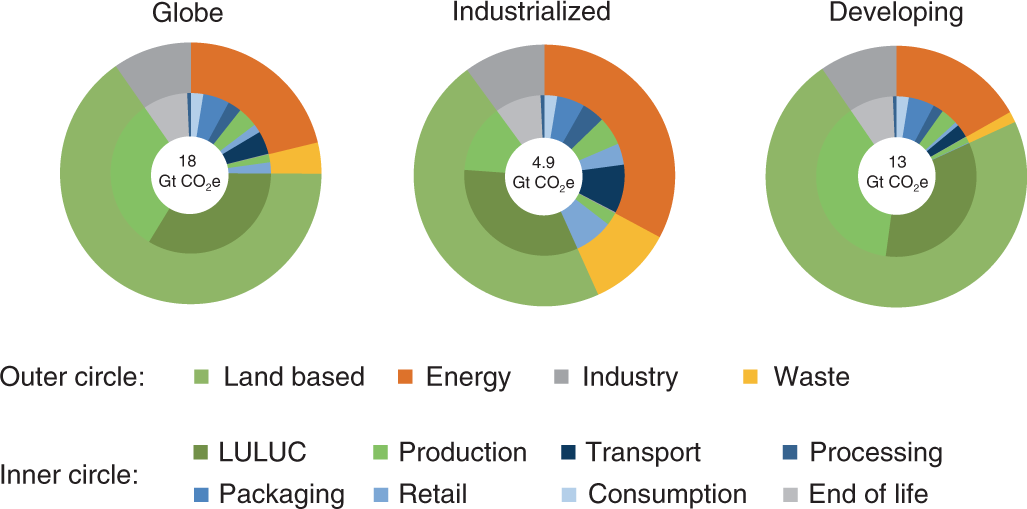



Food Systems Are Responsible For A Third Of Global Anthropogenic Ghg Emissions Nature Food




Reducing Carbon Dioxide Emissions From Electricity Sector Using Smart Electric Grid Applications



Greenhouse Gas Emissions By The United States Wikipedia



1



What Are The Five Greenhouse Gases Quora




Federal Climate Policy To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions
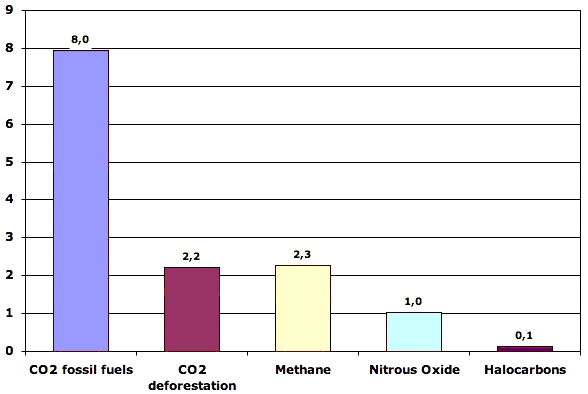



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici
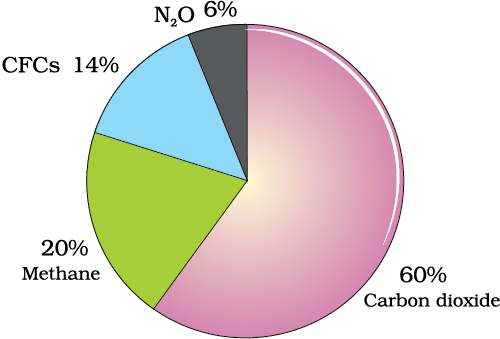



Sections




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




What Is Green House Effect Give Examples For Green House Gases
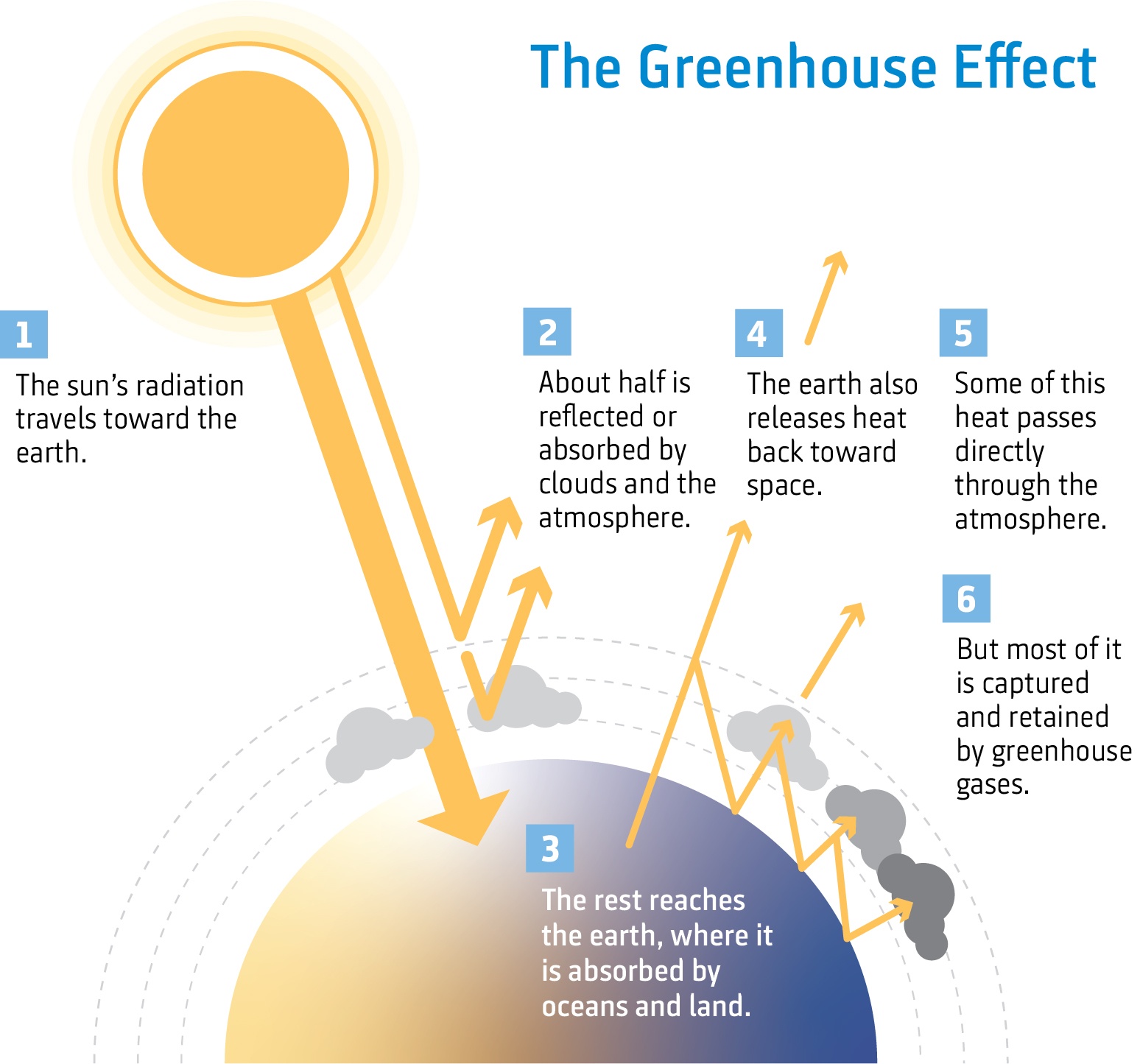



Climate Change The Science Niwa




Greenhouse Gases Responsible For Global Warming Earth Eclipse



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿